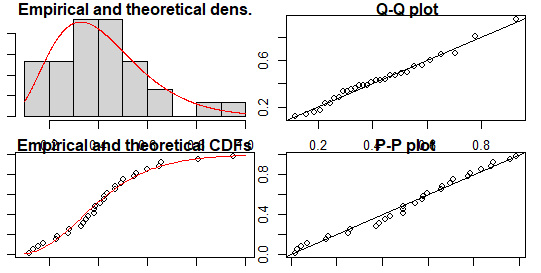
Bootstrapping in R, Inferential statistics employs a technique called bootstrapping that builds random samples of single datasets repeatedly.
Calculating sampling metrics like mean, median, mode, confidence intervals, etc. is made possible by bootstrapping.
Bootstrapping in R
The steps involved in bootstrapping using the R programming language are as follows:
- Decide how many bootstrap samples to use.
- Decide on each sample’s size.
- Choose a random observation from the dataset for each sample, and add it to the sample if the sample size is less than the sample that was selected.
- Calculate the sample’s statistic.
- Calculate each estimated sample value’s mean.
The future of Data Science: Predictions and opportunities »
Techniques for Self-Sufficiency
Two approaches exist for bootstrapping:
Model-based resampling is another name for the technique known as residual resampling. This approach assumes that the model is accurate and that mistakes are uniformly distributed and independent.
Variables are redefined and new variables are utilized to measure the new dependent variables following each resampling.
Bootstrap Pairs: In this technique, sampling is done using pairs of the dependent and independent variables.
Example:
# Load the library
library(boot)
# Creating a function to pass into boot() function
bootFunc <- function(data, i){
df <- data[i, ]
c(cor(df[, 2], df[, 3]),
median(df[, 2]),
mean(df[, 1])
)
}
b <- boot(mtcars, bootFunc, R = 100)
print(b)
# Show all CI values
boot.ci(b, index = 1)
ORDINARY NONPARAMETRIC BOOTSTRAP
Call:
boot(data = mtcars, statistic = bootFunc, R = 100)
Bootstrap Statistics :
original bias std. error
t1* 0.9020329 0.005836535 0.02239087
t2* 6.0000000 0.370000000 0.84870668
t3* 20.0906250 0.025187500 1.03766864
>
> # Show all CI values
> boot.ci(b, index = 1)
BOOTSTRAP CONFIDENCE INTERVAL CALCULATIONS
Based on 100 bootstrap replicates
CALL :
boot.ci(boot.out = b, index = 1)
Intervals :
Level Normal Basic
95% ( 0.8523, 0.9401 ) ( 0.8488, 0.9410 )
Level Percentile BCa
95% ( 0.8631, 0.9553 ) ( 0.8460, 0.9374 )
Calculations and Intervals on Original Scale
Some basic intervals may be unstable
Some percentile intervals may be unstable
Warning : BCa Intervals used Extreme Quantiles
Some BCa intervals may be unstable
How to Perform a Log Rank Test in R » Data Science Tutorials