optim Function in R, we will explore how to apply a general-purpose optimization using the optim function in R programming language.
We will create example data and then demonstrate the usage of the optim function to minimize the residual sum of squares.
optim Function in R
First, let’s create the example data we will use for this tutorial:
# Set a random seed for reproducibility
set.seed(123)
# Create random data
x <- rnorm(500)
y <- rnorm(500) + 0.7 * x
# Combine x and y into a data frame
data <- data.frame(x, y)
# Print the head of the data
head(data)
This code generates a data frame with two numeric variables, x and y.
x y
1 -0.56047565 -0.9942258
2 -0.23017749 -1.1548228
3 1.55870831 2.1178809
4 0.07050839 0.8004172
5 0.12928774 -1.4186651
6 1.71506499 1.1053980
Example: Applying optim Function in R
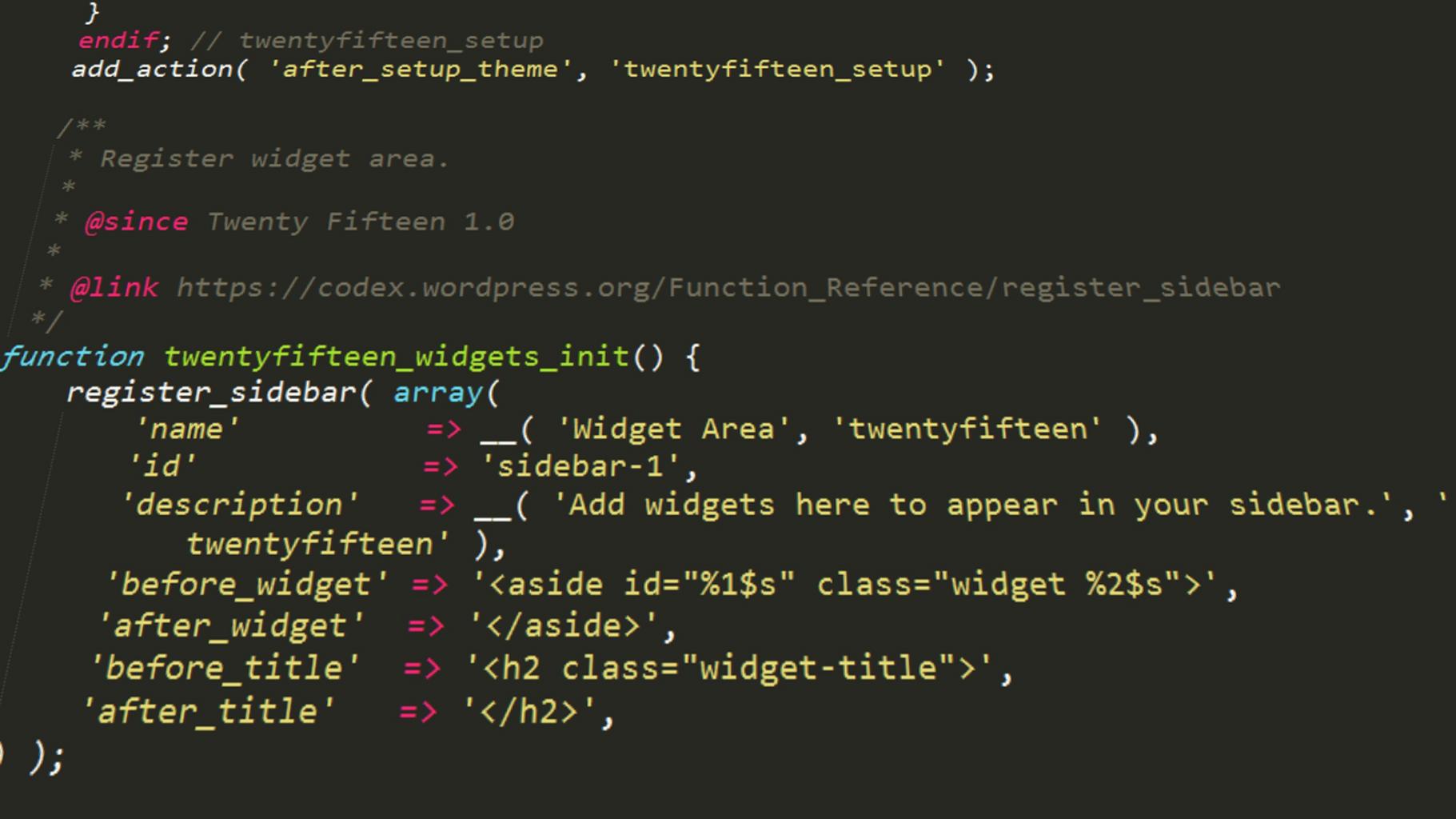
Now, let’s apply the optim function to minimize the residual sum of squares. We will manually create a function for this purpose:
# Manually create a function for residual sum of squares
optm_function <- function(data, par) {
with(data, sum((par[1] + par[2] * x - y)^2))
}
Next, we can use the optim function as shown below.
The par argument specifies the initial values for the parameters to be optimized over, the fn argument specifies our function, and the data argument specifies our data frame.
We store the output of the optim function in the optim_output object:
# Applying optim
optim_output <- optim(par = c(0, 1),
fn = optm_function,
data = data)
Finally, we can visualize our results in a plot. We will compare the results of the optim function with those of a conventional linear model provided by the lm function:
# Set plot parameters par(mfrow = c(1, 2)) # Plot results of the optim function plot(data$x, data$y, main = "optim Function") abline(optim_output$par[1], optim_output$par[2], col = "red") # Plot results of the lm function plot(data$x, data$y, main = "lm Function") abline(lm(y ~ x, data), col = "green")

The resulting plot (Figure 1) should show that both the optim and lm functions returned the same result, indicating that our manual optimization using the optim.
- Apply Central Limit Theorem in R » Data Science Tutorials
- Gamma distribution in R » Data Science Tutorials
- Surprising Things You Can Do With R »
- Bias Variance Tradeoff Machine Learning Tutorial »
- How to Find Unmatched Records in R » Data Science Tutorials