How to Specify Histogram Breaks in R, you may want to specify the number of breaks or bins to use.
How to Specify Histogram Breaks in R
By default, the hist() function uses Sturges’ Rule to determine the optimal number of bins based on the number of observations in the dataset.
However, you can override this default behavior by specifying the breaks argument.
Sturges’ Rule
Sturges’ Rule is a formula that calculates the optimal number of bins to use in a histogram based on the number of observations in the dataset. The formula is:
Optimal Bins = ⌈log2n + 1⌉
where n is the total number of observations in the dataset.
For example, if you have a dataset with 31 observations, Sturges’ Rule would suggest using 6 bins.
Add Footnote to ggplot2 » Data Science Tutorials
Specifying Breaks
If you want to specify a different number of bins to use, you can use the breaks argument in the hist() function.
However, note that R will only use this as a suggestion and may choose to use a different number of bins if it deems it necessary.
To force R to use a specific number of bins, you can use the following code:
hist(data, breaks = seq(min(data), max(data), length.out = n+1))Where n is the desired number of bins.
Example
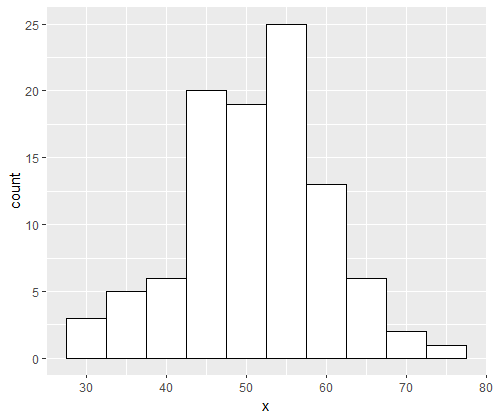
Suppose we have a dataset with 16 values:
data <- c(2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 15, 18, 20, 21)If we use the hist() function without specifying any breaks, R will create a histogram with 5 bins:
hist(data)However, if we try to specify 7 bins using the breaks argument, R will only take this as a suggestion and may choose to use a different number of bins:
hist(data, breaks=7)To force R to use 7 bins, we can use the following code:
hist(data, breaks = seq(min(data), max(data), length.out = 8))This will create a histogram with 7 equally-spaced bins.
Conclusion
While Sturges’ Rule is a useful default behavior for determining the optimal number of bins to use in a histogram, you may need to specify custom breaks depending on your specific dataset and visualization goals.
- Introduction to the five number summary: definition, formulas, and examples
- Effect Sizes for T-Test and ANOVA
- Introduction to Deep Learning
- Regression Analysis
- Business leader’s approach towards Data Science
- Boost Your Resume with Machine Learning Portfolio Projects
- 10 Data analytics Interview Questions and Answer
- Repeated Measures of ANOVA in R Complete Tutorial