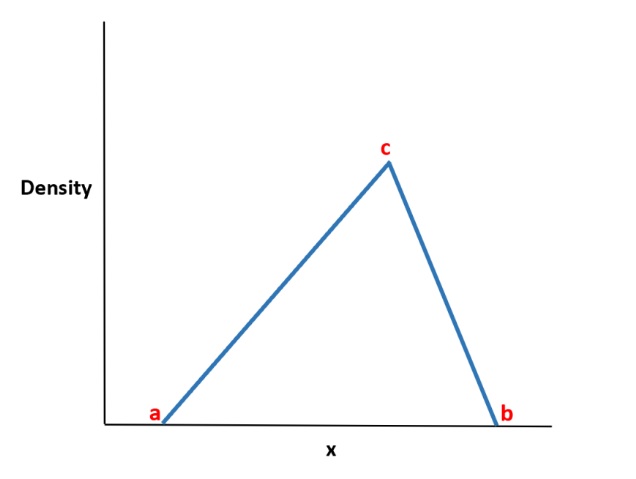
Triangular Distribution in R, A continuous probability distribution with a triangle-shaped probability density function is known as the triangular distribution.
The following three values describe it:
- The bare minimum of a
- The highest value b
- The maximum value c
Triangular Distribution in R

To calculate probabilities for the triangular distribution in R, use the ptri() function from the EnvStats package. Its syntax is as follows.
ptri(q, min = 0, max = 1, mode = 1/2)
where:
q: Quantile of interest
min: The distribution’s smallest possible value
max: The distribution’s top value at its maximum
mode: The distribution’s highest point
The examples that follow demonstrate how to actually utilize this function in R.
Example 1:- Calculating the Probability Less Than Some Value
Consider a restaurant that anticipates a minimum $20,000, a maximum $40,000, and most likely $35,000 in total revenues for the forthcoming week.
What is the chance that the restaurant’s overall sales would be less than $30,000?
To determine this probability, we can use the code below:
library(EnvStats)
Let’s calculate the probability
ptri(q = 30000, min = 20000, max = 40000, mode = 35000) [1] 0.3333333
The likelihood that the restaurant’s total sales fall below $30,000 is.333.
Example 2:-Calculating Probability Greater Than Some Value
Let’s say a store predicts that in any given week, there would be a minimum of 600, a maximum of 3,000, and a likelihood of 2,200 customers.
What is the likelihood that the store will receive more than 2,500 visitors in a given week?
1 - ptri(q = 2500, min = 600, max = 3000, mode = 2200) [1] 0.1302083
About 0.1302083 percent of customers over 2,500 will enter the store.
Further Resources:-
The following tutorials provide guidance on using R to manipulate various probability distributions:
The Multinomial Distribution in R – Data Science Tutorials
The Uniform Distribution in R – Data Science Tutorials
Test for Normal Distribution in R-Quick Guide – Data Science Tutorials